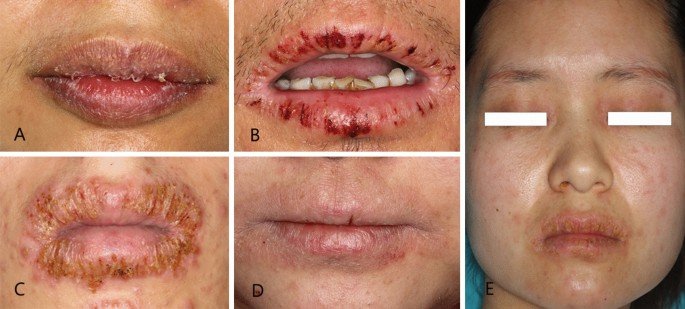
Understanding Cheilitis: Causes, Types, and Management
Cheilitis, or inflammation of the lips, is a common dermatological condition that can arise from various factors. Given the importance of lip health, this article will explore the causes, types, symptoms, and management of cheilitis, drawing from recent research and clinical insights.
What is Cheilitis?
Cheilitis refers to inflammation of the lips characterized by redness, swelling, and sometimes cracking. It can be acute or chronic, depending on the underlying cause, and may affect not only the lips but also the surrounding areas of the mouth.
Types of Cheilitis
Understanding the various types of cheilitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment:
1. Allergic Contact Cheilitis
- Causes: This variety is often triggered by allergens such as certain cosmetics, toothpaste, or food. Notably, some studies have highlighted cases of allergic contact cheilitis resulting from toothpaste ingredients like cocamidopropyl betaine and sodium lauryl sulfate. Van Baelen et al. (2016).
2. Irritant Contact Cheilitis
- Causes: Exposure to irritating substances, including harsh soaps and certain skincare products, can lead to this type of cheilitis. It is more common in individuals with sensitive skin or existing dermatological conditions.
3. Exfoliative Cheilitis
- Characteristics: This chronic condition is characterized by the excessive peeling of the lips. It often affects young adults and can be exacerbated by environmental conditions and stress.
4. Angioedema
- Description: This form of cheilitis involves swelling and can be associated with allergic reactions or food sensitivities.
Symptoms of Cheilitis
Cheilitis symptoms can vary widely but typically include:
- Redness and inflammation
- Cracking or fissuring of the lips
- Itchiness or burning sensation
- Peeling skin
Diagnosis of Cheilitis
Diagnosing cheilitis involves a thorough clinical evaluation, often requiring patient history and examination of symptoms. Dermatologists may recommend skin tests or patch tests to identify specific allergens or irritants contributing to the condition Lugovic-Mihic et al. (2020).
Treatment and Management
Effective management of cheilitis depends on its underlying cause:
1. Avoiding Irritants
- Identify and avoid products that trigger symptoms, such as certain lip balms or toothpastes.
2. Topical Treatments
- Hydrocortisone Cream: Used to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Barrier Creams: Products like petroleum jelly can help protect the lip’s outer layer.
3. Moisturization
- Regular application of moisturizers can combat dryness that exacerbates symptoms. Look for products free from allergens and fragrances.
4. Oral Medications
- In cases where cheilitis is linked to underlying skin conditions like atopic dermatitis, dermatologists may prescribe systemic medications Furue et al. (2017).
5. Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies
- Some cases of cheilitis may arise from a lack of certain nutrients, such as vitamin B2 or iron. A balanced diet can help prevent such deficiencies.
Lifestyle Tips for Lip Care
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to maintain skin hydration.
- Shield Lips from Sun: Use lip balm with SPF to protect against UV rays.
- Utilize Humidifiers: In dry climates, humidifiers can help maintain moisture levels in the air.
Conclusion
Cheilitis is a multifaceted condition with various causes and types. Understanding the key symptoms and potential triggers is essential for effective management. Anyone experiencing persistent or severe symptoms should consult a healthcare professional to explore appropriate treatment options. For further understanding of skin conditions, consider reading more on eczema or atopic dermatitis.
By being informed about the causes and management of cheilitis, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy lips and alleviate discomfort.